Immunohistochemistry
DAB staining immunohistochemistry
After washes with phosphate buffer (PB), the stored sections are transferred to TBS (TRIS buffered physiological saline, pH=7.4) for further incubation steps, as all sera are diluted in TBS and washed with TBS (3X10 min) between each incubation step. For endogenous peroxidase blocking, a 1% solution of H2O2 is used. For non-specific binding site blocking: normal horse or goat serum (NHS, NGS) or bovine serum albumin (BSA) is used.
This is followed by incubation in primary sera for 2 days at 4°C. Depending on the study, several neuronal, glial and vascular elements can be labelled. The specificity of the antibodies has been tested by the source. We also tested the staining patterns of all antibodies on animal and human tissues at multiple concentrations to determine the optimal conditions of use. In cases where multiple antibodies were used, we compared the staining of each antibody in separate experiments to make sure they stained the same. We always use the same antibody in a series of experiments.
Then we put the biotinylated secondary serum that recognizes the primary serum on the sections. This is followed by incubation with the avidin-biotin- horseradish peroxidase complex (ABC). Sections are washed in TBS and preincubated in TRIS buffer (TB, pH=7.6) and DAB (3,3'-diaminobenzidine-4HCl) at 0.05M concentration for 20 minutes, then preincubated with 0.01% hydrogen peroxide added to the DAB chromogen. A brown reaction end product accumulates in immunopositive cells.
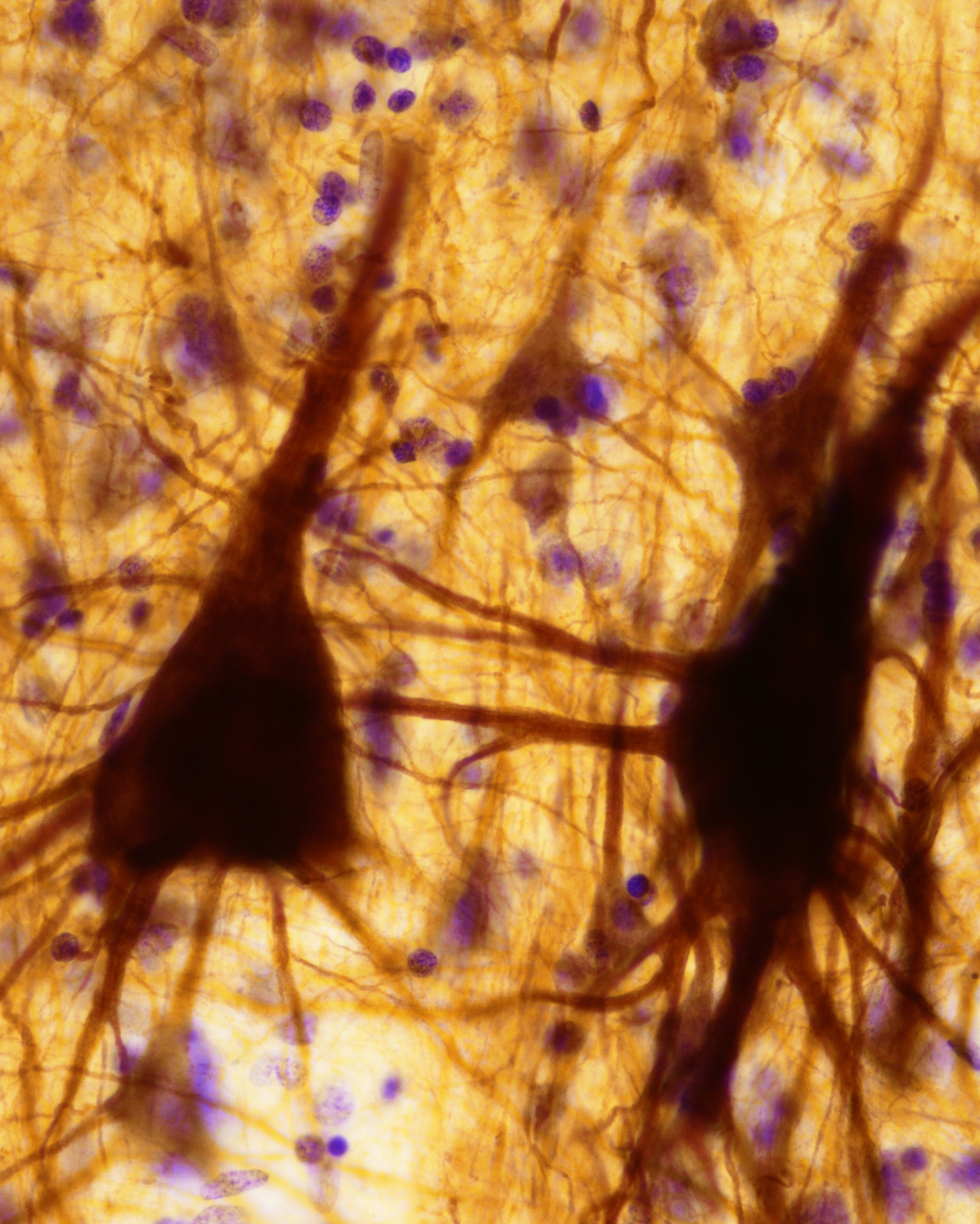
Fig. 1. Human giant pyramidal cells (Betz cells) labeled with SMI32 immunostaining, and Nissl counterstaining (structures in purple).
Sections are osmified (1% OsO4, variable time), dehydrated in a series of rising ethanol (1% uranyl acetate in 70% alcohol, 40 min) and dehydrated in acetonitrile, then embedded in Durcupan (ACM; Fluka).
After light microscopy, the areas requiring detailed examination are embedded, serial sections are taken with an ultramicrotome and examined by electron microscopy. Control and pathological tissues are subjected to the same procedures.
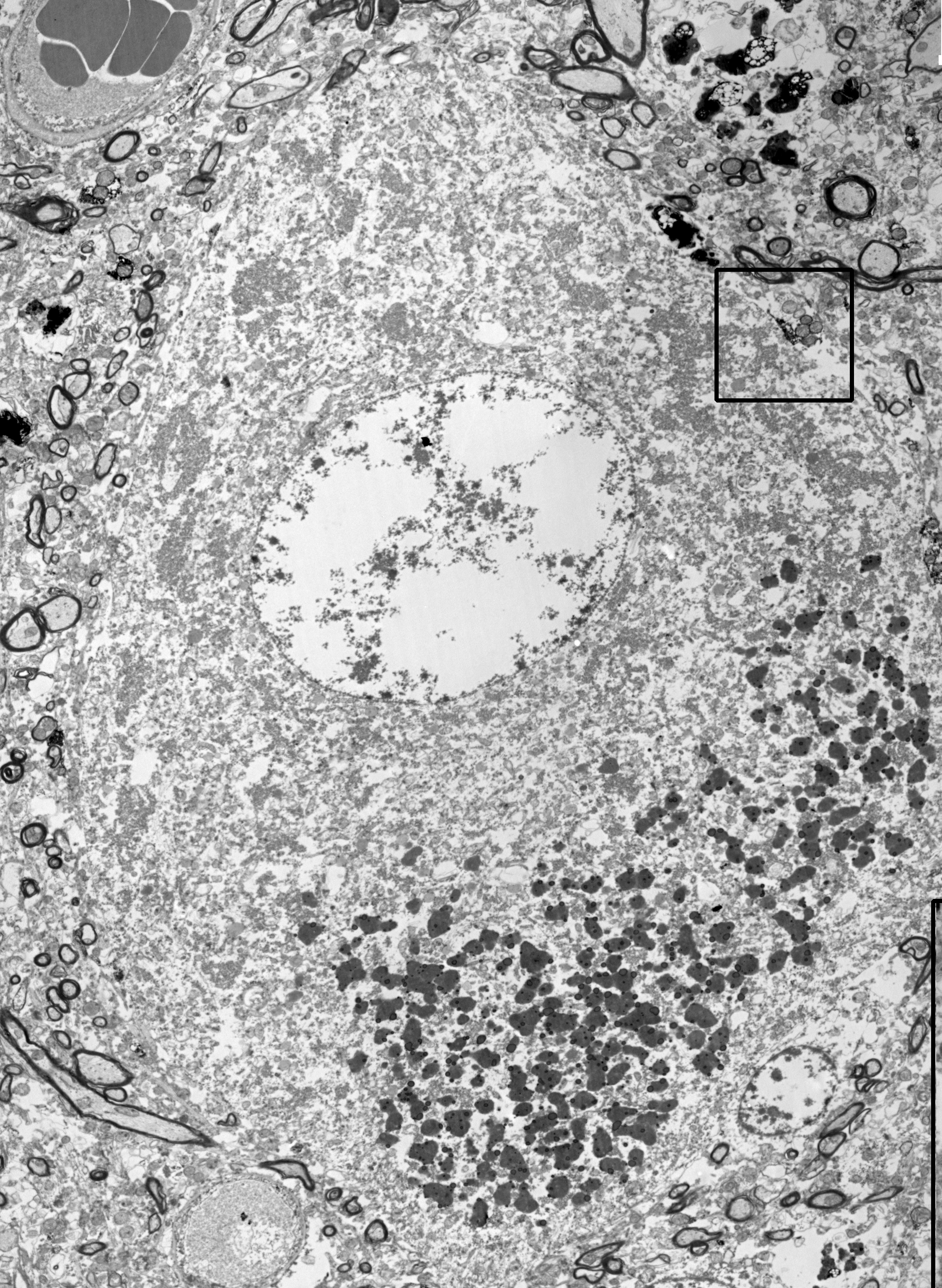
Fig.2. Electron micrograph of a human Betz cell labelled with parvalbumin (PV).
Multiple fluorescence immunostaining
The steps are performed in TBS solution as before, with washing periods between incubation steps. Incubation with 1% H2O2 solution reduces the autofluorescence of the sections. Aspecific antigen blocking is performed in BSA solution with an additional 0.1% Triton to increase cell membrane permeability. The primary solutions are incubated on the sections for 2 days at 4 °C on a laboratory shaker, with 2-3 primary antibodies added to the incubation solution. Their specificity and the required concentration are checked as described above. The appropriate secondary antibodies are incubated for 1 day at 4 °C or for 3 hours at room temperature in the dark, depending on the experimental series. The sections are then kept in a distilled aqueous solution containing 3 mmol/l copper sulphate, 50 mmol/l ammonium acetate, pH=5, according to Schnell et al. 1999, for 40 min to reduce their autofluorescence. The sections are then covered. Sections are examined using the laboratory's Nikon Ci-L microscope or confocal systems (Nikon A1R, C2) and 3DHistech slide scanners available at the IEM Light Microscopy Center.
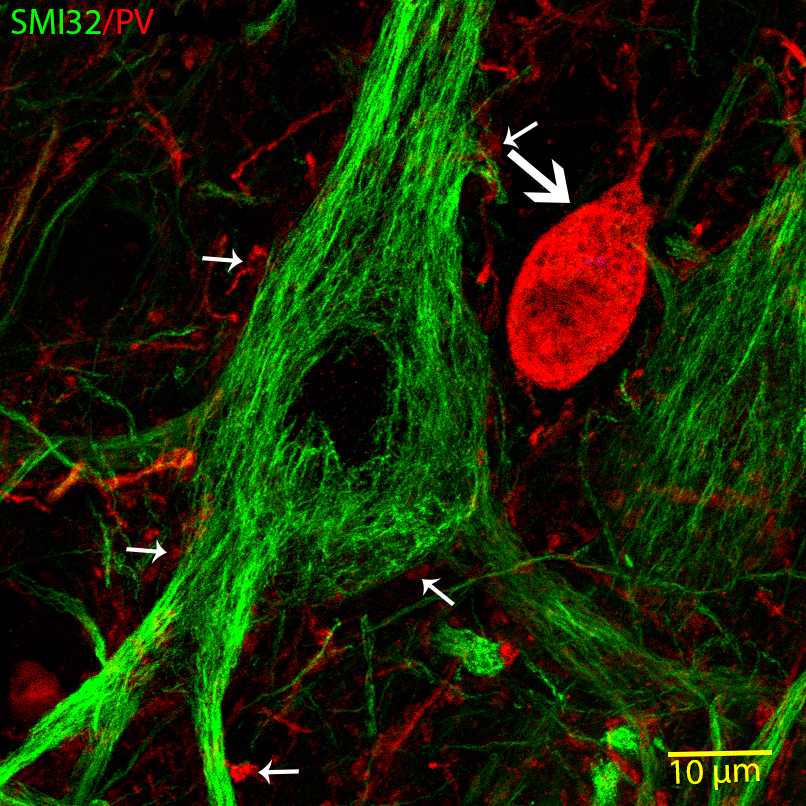
Fig.3. High magnification confocal image of a human giant pyramidal cell (Betz cell) labelled with SMI32-antibody (green) and a neighbouring parvalbumin (PV)-immunopositive (red) interneuron (big arrow). The small arrows show PV-immunopositive perisomatic terminals.






