Mechanisms of neuro-immuno interactions and their role in neurological diseases
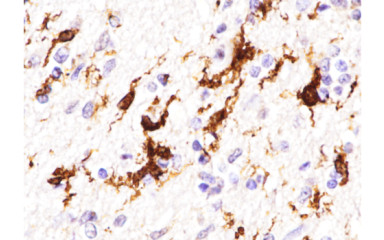
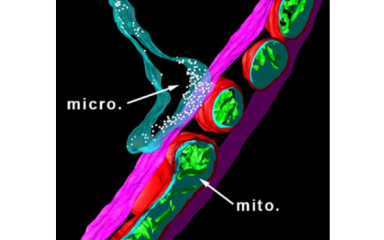
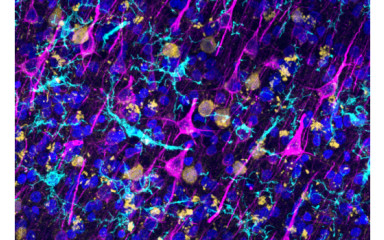
It is now clear that the pathophysiology of stroke, neurodegenerative diseases, developmental neurological and psychiatric disorders is characterised by a prominent role of the neuro-immune system's bilateral interactions, including inflammatory processes. The role of immune processes in the normal development and functioning of the central nervous system has been demonstrated. But it is important to emphasize, that common chronic diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) are not only associated with increased systemic inflammation but also represent a major risk factor for the development of various neurological diseases. Early life infections, insults and metabolic abnormalities trigger an inflammatory response with long-lasting effects, which plays a role in the development of several pathologies (ADHD and other psychiatric disorders). Therefore, new effective diagnostic and therapeutic methods cannot be developed without a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms of neuro-immune processes. One of the most important contributors to these is the microglia, the main immune cell of the central nervous system, which plays a major role in both neurodevelopment and pathological processes.
Our institute has a number of internationally leading publications on this topic, which have revealed the role of microglia in the regulation of neuronal activity, brain injury and the inhibition of central viral infections. The Institute is also investigating the mechanisms underlying the inflammatory processes responsible for neurodegenerative disorders resulting from COVID-19 and is supported by its unique human brain bank.